-

 $9.99
$9.99Introduction to Curcumin and Turmeric Turmeric, a vibrant yellow spice derived from the rhizome of the Curcuma longa plant, has been utilized for centuries in various cultural cuisines, particularly within South Asian and Middle Eastern traditions. Its distinct flavor and warm aroma make it a staple ingredient in numerous culinary […]
-

 $9.99
$9.99Understanding Magnesium Glycinate Magnesium glycinate is a compound formed from magnesium and glycine, an amino acid, resulting in a highly bioavailable form of magnesium. Magnesium plays a crucial role in numerous biological processes, including muscle function, nerve signaling, and the regulation of various physiological functions. By binding to glycine, magnesium […]
-

 $15.99
$15.99Prickly pear leaf extract is derived from the Opuntia cactus, known for its rich nutritional profile. This supplement provides antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that contribute to overall health. Its ability to promote hydration and support healthy digestion makes it a popular choice among health enthusiasts.
-

 $24.99
$24.99Vitamins and minerals are essential nutrients that play significant roles in maintaining overall health and well-being. These organic compounds and inorganic elements are required in small quantities but are vital for various physiological processes in the body. Vitamins are classified into two categories: water-soluble, which includes Vitamin C and the B vitamins, and fat-soluble, which encompasses Vitamins A, D, E, and K. Minerals, on the other hand, are inorganic substances, such as zinc, which the body also requires to function optimally.
-

 $19.99
$19.99Herbal supplements have been an integral part of traditional medicine for centuries, utilized in various cultures across the globe for their therapeutic properties. These natural products derive from plants, herbs, and botanicals, and have been employed to promote well-being, enhance vitality, and alleviate a range of ailments. As healthcare trends shift towards more holistic approaches, the use of herbal supplements has increasingly gained traction in contemporary health practices. This rising popularity can be attributed to a growing demand for natural alternatives to pharmaceutical solutions, aimed at fostering better health without synthetic compounds.
-

 $79.99
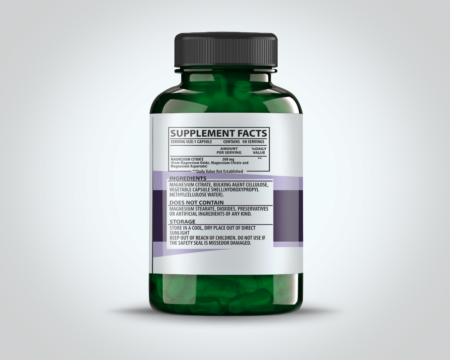
$79.99AllHealth Magnesium Citrate is a highly bioavailable form of magnesium, renowned for its efficiency in delivering essential nutrients to the body. Magnesium, an essential mineral, plays a crucial role in numerous physiological functions, making it vital for overall health. This form of magnesium is derived from the combination of magnesium and citric acid, which enhances its absorption and effectiveness compared to other forms such as magnesium oxide or magnesium sulfate.
-

 $14.99
$14.99Collagen is a vital protein that serves as a primary structural component in various tissues throughout the human body. It is the most abundant protein, accounting for approximately 30% of the total protein content. Collagen fibers provide strength, elasticity, and support to the skin, bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments, making it essential for overall health and physical structure. There are at least 28 types of collagen, with Type I, Type II, and Type III being the most prevalent. Type I collagen, which is predominantly found in skin, tendons, and bones, provides tensile strength. Type II collagen is primarily located in cartilage, playing a crucial role in joint health and function. Type III collagen is often found alongside Type I in skin and blood vessels, contributing to the elasticity and firmness of these structures.
-

 $12.99
$12.99Maca, scientifically known as Lepidium meyenii, is a root vegetable native to the high altitudes of the Andes Mountains in Peru. Historically, maca has been cultivated for over 2,000 years and was a staple in the diet of indigenous populations. The ancient Inca warriors reputedly consumed maca to enhance their endurance and strength before heading into battle. Traditional indigenous cultures have long revered maca for its nutritional and medicinal properties, utilizing it to boost energy, improve fertility, and address various health concerns.
-

 $9.99
$9.99AllHealth Magnesium Citrate is a highly bioavailable form of magnesium, renowned for its efficiency in delivering essential nutrients to the body. Magnesium, an essential mineral, plays a crucial role in numerous physiological functions, making it vital for overall health. This form of magnesium is derived from the combination of magnesium and citric acid, which enhances its absorption and effectiveness compared to other forms such as magnesium oxide or magnesium sulfate.
-

 $9.99
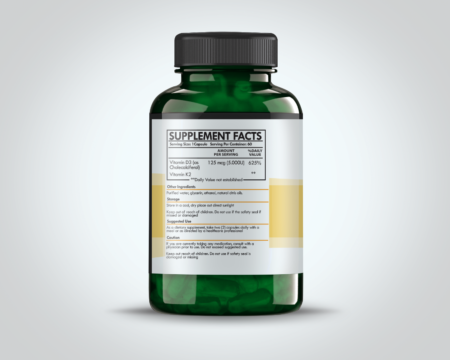
$9.99Vitamin K2, a fat-soluble vitamin, is a lesser-known subclass of Vitamin K, which primarily exists in the forms of K1 (phylloquinone) and K2 (menaquinone). Vitamin K2’s primary function is to activate proteins that regulate where calcium ends up in the body. This control is vital for maintaining bone density and preventing arterial calcification, thereby playing a crucial role in cardiovascular health.
On the other hand, Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is an essential fat-soluble vitamin produced endogenously when ultraviolet rays from sunlight strike the skin and trigger vitamin D synthesis. Vitamin D3 is crucial for calcium absorption in the intestines, immune system support, and modulation of cell growth. Given its wide-ranging influence, a deficiency in Vitamin D3 can contribute to a variety of health issues, including osteoporosis and compromised immune defenses.
-

 $7.99
$7.99Vitamins K2 and D3 are crucial micronutrients that play significant roles in maintaining overall health. Vitamin K2, a subset of the vitamin K group, is structurally characterized by its various menaquinone forms, with MK-7 being the most studied. Vitamin D3, or cholecalciferol, belongs to the vitamin D family and is known for its synthesis in the skin upon exposure to sunlight.
-

 $8.99
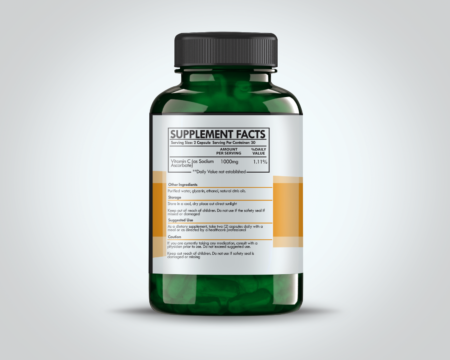
$8.99Vitamin C, widely recognized as ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a critical role in maintaining the health of various bodily systems. Known for its potent antioxidant properties, Vitamin C is crucial for the synthesis of collagen, the absorption of iron, the proper functioning of the immune system, wound healing, and the maintenance of cartilage, bones, and teeth.
-

 $7.99
$7.99Magnesium citrate is an essential compound derived from the mineral magnesium combined with citric acid, offering a highly bioavailable form of magnesium. Magnesium is a crucial element in numerous physiological processes, including nerve function, muscle contraction, and bone development. The human body requires magnesium to maintain normal blood pressure, support a healthy immune system, and facilitate over 300 enzymatic reactions.
-

 $9.99
$9.99Maca, scientifically known as Lepidium meyenii, is a root vegetable that has been cultivated for thousands of years in the high-altitude regions of the Andes Mountains in Peru. This hardy plant has long been an integral part of the diet and traditional medicine of indigenous people, who have relied on its nutritional and medicinal properties. Historically, maca root was consumed for its ability to enhance energy, stamina, and fertility, and it was also used to support overall health.
-

 $9.99
$9.99Echinacea, a genus of flowering plants in the daisy family, is renowned for its immune-boosting properties. Native to North America, this perennial plant thrives in prairies and open wooded areas, marked by its striking, cone-shaped flower heads and bright pink or purple petals. Echinacea comprises several species, with Echinacea purpurea, Echinacea angustifolia, and Echinacea pallida being the most widely recognized and utilized in herbal medicine. Each species has distinct botanical characteristics and varying levels of bioactive compounds, influencing their respective therapeutic applications.
-

 $11.99
$11.99Curcumin is the primary active compound found in turmeric, a spice that has been extensively used in traditional medicine for thousands of years. Chemically, curcumin belongs to a group of compounds known as curcuminoids, and it is celebrated for its vibrant yellow color, which is a distinguishing feature in both culinary and medicinal applications.
-

 $13.99
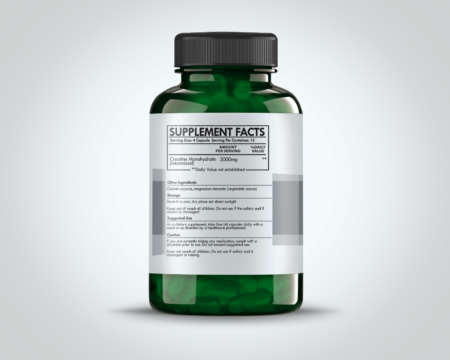
$13.99Creatine is a naturally occurring compound that plays a pivotal role in energy production within muscle cells. It is synthesized primarily in the liver, kidneys, and pancreas from amino acids like arginine, glycine, and methionine. Stored predominantly in skeletal muscle, creatine serves as a readily available energy source during short bursts of high-intensity activities, such as weight lifting, sprinting, and other explosive movements.
-

 $12.99
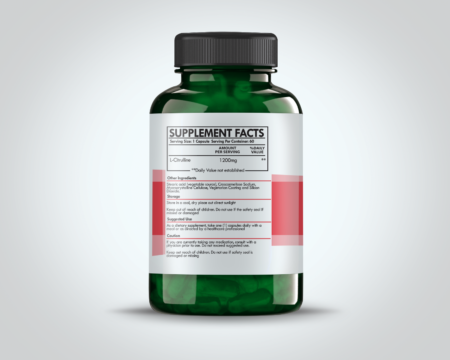
$12.99Citrulline is a non-essential amino acid that plays a significant role in various physiological processes in the human body. Naturally, it can be found in high amounts in watermelon, which serves as one of the most potent natural sources of citrulline. Apart from dietary intake, the body also produces citrulline internally as part of the urea cycle. This cycle is critical for the removal of ammonia, a potentially harmful byproduct of protein metabolism, from the body. Citrulline aids in converting ammonia into urea, which is subsequently excreted through urine.
-

 $9.99
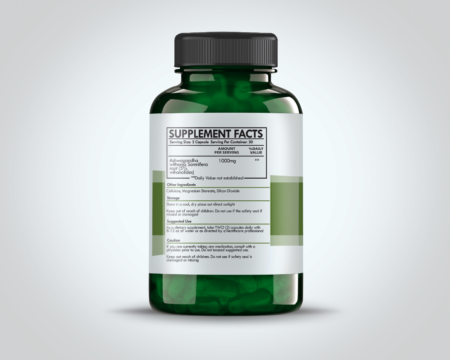
$9.99Ashwagandha, scientifically known as Withania somnifera, is a revered herb in the pantheon of Ayurvedic medicine, with origins tracing back over 3,000 years. Native to the Indian subcontinent, this robust plant has been cherished for its multifaceted healing properties and its esteemed role in promoting vitality and overall well-being. The term “Ashwagandha” is derived from Sanskrit, meaning “smell of the horse,” a nod to its potent smell and the belief that it imparts the strength and vigor of a horse.
New Brand