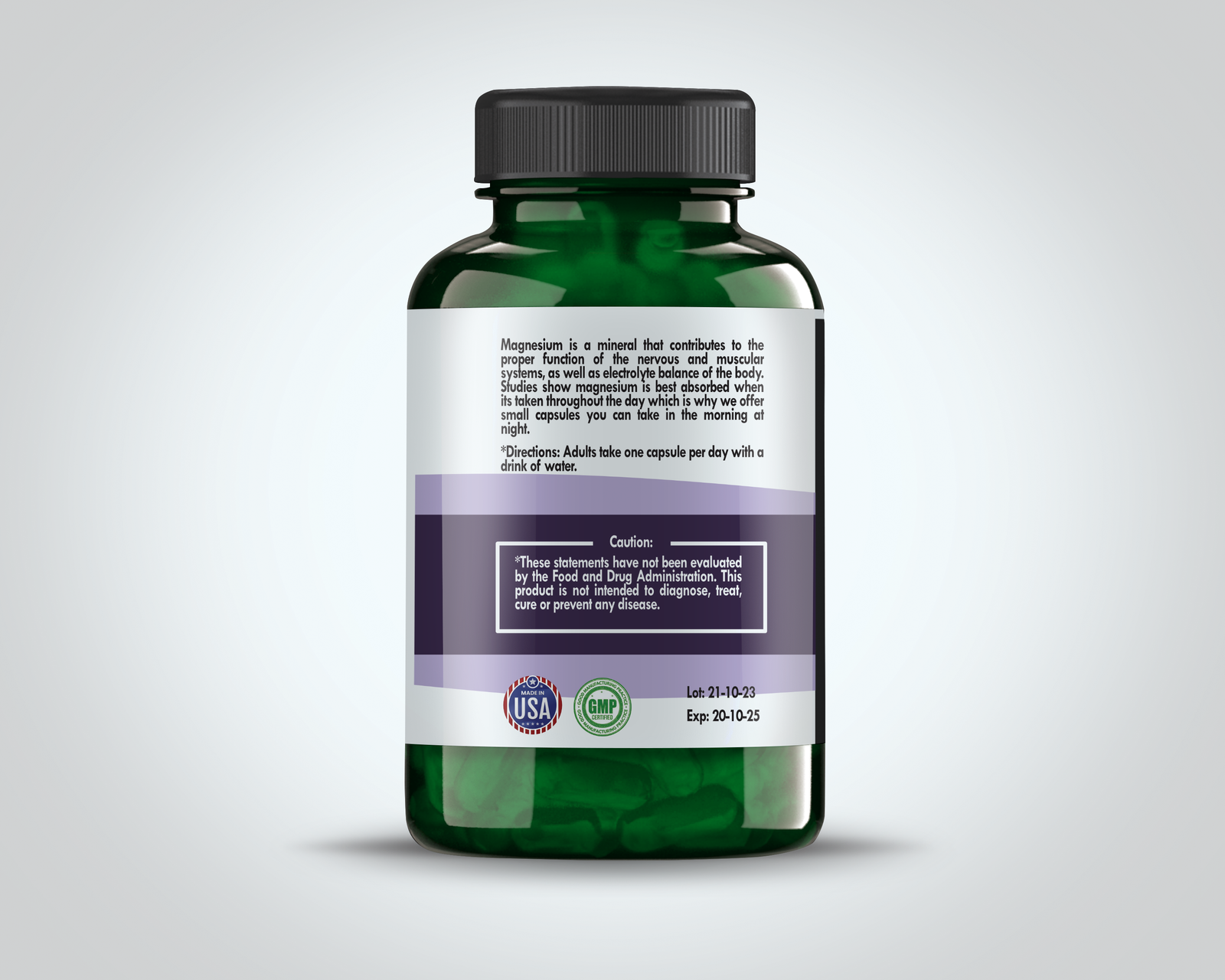
Magnesium citrate is an essential compound derived from the mineral magnesium combined with citric acid, offering a highly bioavailable form of magnesium. Magnesium is a crucial element in numerous physiological processes, including nerve function, muscle contraction, and bone development. The human body requires magnesium to maintain normal blood pressure, support a healthy immune system, and facilitate over 300 enzymatic reactions.
Nutraplus Magnesium Citrate
$7.99
Información adicional
| color | Black, Blue, Brown, Burgundy, Gray, Mint |
|---|---|
| size | XS, S, M, L |
Descripción
Introduction to Magnesium Citrate
Magnesium citrate is an essential compound derived from the mineral magnesium combined with citric acid, offering a highly bioavailable form of magnesium. Magnesium is a crucial element in numerous physiological processes, including nerve function, muscle contraction, and bone development. The human body requires magnesium to maintain normal blood pressure, support a healthy immune system, and facilitate over 300 enzymatic reactions.
The unique formulation of magnesium citrate enhances its absorption rate, making it a preferred choice for supplementation. Unlike other forms of magnesium, magnesium citrate is known for its efficiency in increasing blood magnesium levels swiftly. This effectiveness stems from its water-soluble nature, which allows for better absorption through the intestinal wall.
Common uses of magnesium citrate include alleviating symptoms of constipation, as it acts as an osmotic laxative by attracting water into the intestines, thus promoting bowel movement. Additionally, magnesium citrate is frequently recommended for individuals looking to support cardiovascular health, improve energy levels, and mitigate symptoms of magnesium deficiency such as muscle cramps and chronic fatigue.
Beyond these core benefits, magnesium citrate is utilized in medical settings to prepare the bowel for surgical procedures or colonoscopies. It is also employed as a dietary supplement to ensure adequate magnesium intake, especially for those who may have increased needs due to factors like age, diet, or specific health conditions.
This guide delves into the multifaceted benefits of magnesium citrate, exploring its diverse uses and potential advantages over other forms of magnesium supplements. In the sections that follow, we will provide an in-depth analysis of its health benefits, its role in various bodily functions, and practical advice on how to incorporate it effectively into your wellness routine.
Health Benefits of Magnesium Citrate
Magnesium citrate offers numerous health benefits, playing a crucial role in various bodily functions. One of its primary uses is in promoting digestive health, especially in alleviating constipation. As a natural laxative, magnesium citrate works by attracting water into the intestines, softening stool and making bowel movements easier. This mechanism is particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing occasional or chronic constipation, providing a gentle yet effective solution.
Apart from its digestive benefits, magnesium citrate significantly impacts muscle function. Magnesium is essential for muscle contraction and relaxation, helping to prevent cramps and spasms. This mineral also aids in the synthesis of proteins, which are vital for muscle repair and growth. Additionally, it supports nerve function by facilitating the transmission of nerve impulses, which is crucial for overall neurological health.
Bone health is another area where magnesium citrate proves beneficial. Magnesium is a key component of bone structure, contributing to bone density and strength. Adequate magnesium intake is linked to a lower risk of osteoporosis and fractures, particularly in older adults. Furthermore, magnesium citrate plays a role in the regulation of calcium levels in the body, ensuring the proper deposition of calcium in bones rather than in soft tissues.
Cardiovascular health also benefits from magnesium citrate. Magnesium helps maintain a regular heartbeat, supports blood vessel function, and regulates blood pressure. Studies have demonstrated that adequate magnesium levels can reduce the risk of hypertension, heart attack, and stroke. Clinical trials have provided substantial evidence supporting the role of magnesium in promoting heart health, making magnesium citrate an important supplement for cardiovascular wellness.
In summary, the health benefits of magnesium citrate are well-documented and supported by scientific research. Its contributions to digestive health, muscle and nerve function, bone integrity, and cardiovascular health make it a valuable addition to a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle.
How to Use Magnesium Citrate
Incorporating magnesium citrate into your daily routine can be straightforward with the right approach and knowledge. Magnesium citrate is commercially available in various forms, including liquid, powder, and capsules. The choice of form largely depends on personal preferences and sometimes the specific health objectives being targeted.
For general supplementation aimed at maintaining optimal magnesium levels, the typical recommended dosage ranges from 200 mg to 400 mg per day. It is often advised to take this supplement with meals to enhance absorption and reduce the risk of gastrointestinal upset. Liquid forms of magnesium citrate can be mixed with water or juice, whereas powders are usually dissolved in water before consumption. Capsules provide the convenience of pre-measured doses that can be taken directly with water.
When using magnesium citrate as an acute treatment for constipation, a higher dosage may be recommended, usually under the guidance of a healthcare provider. In such cases, a single dose ranging from 240 mL to 300 mL of a liquid solution may be taken. This is typically done on an empty stomach to facilitate quicker action, often resulting in bowel movements within 30 minutes to 6 hours.
Timing the intake of magnesium citrate is essential for maximizing its efficacy and minimizing potential side effects. For sleep support or muscle relaxation, taking the supplement in the evening may be beneficial due to its calming effects. Conversely, for constipation relief, mornings might be more suitable. It is crucial to remain hydrated while using magnesium citrate, as it can have a diuretic effect.
Potential interactions with other medications should not be overlooked. Magnesium citrate can interact with antibiotics, certain blood pressure medications, and muscle relaxants, among others. Ensuring a time gap of at least two hours between taking magnesium citrate and any other medication can help mitigate these interactions.
Lastly, consulting with a healthcare provider before beginning any new supplement regimen is of paramount importance. This helps tailor the dosage and form of magnesium citrate to individual health needs and prevents potential adverse reactions. Adopting a careful, informed approach ensures that incorporating magnesium citrate into your routine is both safe and effective.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
While magnesium citrate is generally well-tolerated and considered safe for most individuals, it is not without its potential side effects. Common side effects include gastrointestinal discomfort, such as diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and nausea. These are typically mild and transient, but they can be bothersome for some individuals.
More serious side effects, though rare, may occur. These include allergic reactions characterized by symptoms such as rash, itching, swelling (especially of the face, tongue, or throat), severe dizziness, or trouble breathing. If any of these symptoms are observed, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
Interactions with other medications are another important consideration. Magnesium citrate may affect the absorption of certain drugs, including antibiotics and medications for osteoporosis. To avoid interactions, it is advisable to take magnesium citrate at least two hours before or after other medications.
When experiencing any side effects, it is essential to discontinue use and consult with a healthcare provider. Adherence to recommended dosages plays a critical role in minimizing risks. Overconsumption of magnesium citrate can lead to more severe complications, such as hypermagnesemia, which is characterized by symptoms like muscle weakness, irregular heartbeat, and breathing difficulties. Therefore, following dosage guidelines is imperative.
Certain individuals should exercise caution or altogether avoid magnesium citrate. Those with kidney issues, such as chronic kidney disease, are at an increased risk of magnesium toxicity due to impaired kidney function. Pregnant women should also consult their healthcare provider before using magnesium citrate to ensure it is safe for their specific situation. Individuals with diagnosed gastrointestinal disorders should seek professional advice before including this supplement in their routine.
In conclusion, while magnesium citrate offers multiple health benefits, being aware of potential side effects and taking necessary precautions can help ensure its safe and effective use.
“`












Valoraciones
No hay valoraciones aún.