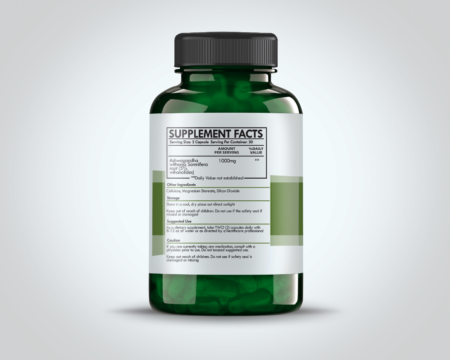
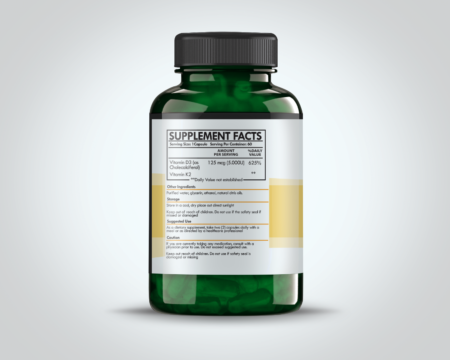
Echinacea, a genus of flowering plants in the daisy family, is renowned for its immune-boosting properties. Native to North America, this perennial plant thrives in prairies and open wooded areas, marked by its striking, cone-shaped flower heads and bright pink or purple petals. Echinacea comprises several species, with Echinacea purpurea, Echinacea angustifolia, and Echinacea pallida being the most widely recognized and utilized in herbal medicine. Each species has distinct botanical characteristics and varying levels of bioactive compounds, influencing their respective therapeutic applications.
Nutraplus Echinacea
$9.99
Descripción
Introduction to Echinacea
Echinacea, a genus of flowering plants in the daisy family, is renowned for its immune-boosting properties. Native to North America, this perennial plant thrives in prairies and open wooded areas, marked by its striking, cone-shaped flower heads and bright pink or purple petals. Echinacea comprises several species, with Echinacea purpurea, Echinacea angustifolia, and Echinacea pallida being the most widely recognized and utilized in herbal medicine. Each species has distinct botanical characteristics and varying levels of bioactive compounds, influencing their respective therapeutic applications.
Echinacea purpurea, known as the purple coneflower, is characterized by its large, broad leaves and relatively tall stature. Echinacea angustifolia, or narrow-leaved coneflower, features slender leaves and thrives in dry, rocky soils. Echinacea pallida, distinguished by its pale pink flowers and drooping petals, is less common but still valued for its medicinal properties. Despite their differences, all species contain a rich array of phytochemicals, including alkamides, glycoproteins, polysaccharides, and essential oils, contributing to their health benefits.
Historically, the indigenous peoples of North America utilized Echinacea for its diverse medicinal properties. It was used to treat snake bites, insect stings, and various infections. Echinacea’s use in traditional medicine involved both oral and topical applications, reflecting its versatility as a natural remedy. The knowledge and practices surrounding Echinacea were passed down through generations, maintaining its relevance in herbal healing traditions.
The resurgence of interest in herbal medicine during the 20th century brought Echinacea to global prominence. Modern scientific research has validated many of the traditional uses of Echinacea, particularly its role in supporting immune function and combating respiratory infections. Today, Echinacea is a staple in dietary supplements, teas, and tinctures, fostering a growing appreciation for this ancient medicinal plant.
“`
Health Benefits of Echinacea
Echinacea, a flowering plant commonly known for its immune-boosting properties, has garnered significant attention in the health and wellness community. Numerous studies have been conducted to explore the medicinal potential of this plant, particularly its effects on the immune system. Echinacea is believed to stimulate the production of white blood cells, which play a crucial role in fighting off infections. This has made it a popular supplement during flu season and times when colds and upper respiratory infections are prevalent.
Scientific evidence supports the claim that Echinacea can reduce the severity and duration of colds. A meta-analysis of 14 studies published in ‘The Lancet Infectious Diseases’ found that Echinacea supplementation decreased the odds of developing a cold by 58% and shortened the duration of a cold by an average of 1.4 days. These findings emphasize Echinacea’s significant role in supporting immune health and offer a compelling reason to incorporate it into one’s health regimen, especially during peak cold seasons.
Beyond its immune-boosting capabilities, Echinacea possesses additional health benefits worth noting. The plant exhibits potent anti-inflammatory properties, which can aid in reducing inflammation in various parts of the body. These properties make it a potential natural remedy for inflammatory conditions. Furthermore, Echinacea has demonstrated antiviral properties that may inhibit the replication of viruses, adding another layer of defense during viral outbreaks.
Antioxidant properties are also a notable aspect of Echinacea, contributing to overall cellular health by combating oxidative stress and free radicals. This quality not only supports immune function but also promotes general well-being. Moreover, research has indicated that Echinacea may have a positive impact on skin health and wound healing. Topical applications of Echinacea extracts have shown promise in accelerating the healing process of minor wounds and reducing skin inflammation.
In summary, Echinacea stands out as a versatile and beneficial plant with a variety of health advantages. Its immune-enhancing, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and antioxidant properties, coupled with potential skin health benefits, make it a valuable addition to natural health practices.
How to Use Echinacea
Echinacea can be a versatile addition to your daily wellness routine, offering multiple forms that cater to diverse preferences and needs. Available in forms such as teas, tinctures, capsules, and topical applications, Echinacea is accessible and convenient for various uses. Teas and tinctures are popular for those who prefer a liquid supplement, while capsules serve as an easy and precise dosing option.
To incorporate Echinacea teas, steep one teaspoon of dried Echinacea root or leaves in a cup of hot water for 10-15 minutes. This preparation can be consumed two to three times daily, especially during the onset of cold or flu symptoms. For tinctures, follow the recommended dosage on the product label, typically ranging from 20 to 30 drops up to three times a day. Capsules usually offer a standardized dosage of Echinacea extract; generally, one to two capsules daily are sufficient, but it is essential to adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Topical applications of Echinacea, such as creams and ointments, can be valuable in soothing skin irritations, wounds, or inflammations. Apply a thin layer to the affected area once or twice daily, depending on the severity of the condition. Always perform a patch test beforehand to ensure there is no allergic reaction.
Selecting high-quality Echinacea products requires scrutinizing labels for ingredients, ensuring the presence of Echinacea purpurea or Echinacea angustifolia. Opt for products tested for purity and potency, ideally verified by third-party certifications. Organic and non-GMO labels can also indicate a higher standard of quality.
Contraindications include potential allergic reactions, particularly for individuals with allergies to plants in the daisy family. Pregnant or breastfeeding women and those with autoimmune disorders should consult healthcare professionals before use. Additionally, prolonged use beyond eight weeks is generally discouraged to prevent potential adverse effects.
As an easy-to-follow recipe, try creating an Echinacea-infused honey. Combine one part dried Echinacea root with two parts raw honey in a glass jar. Let the mixture sit for two weeks, shaking it occasionally, before straining out the root. This Echinacea honey can be blended into teas or taken by the spoonful to bolster immunity.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Using Echinacea, while generally regarded as safe for short-term use, can present certain side effects and necessitates taking precautions. Common side effects associated with the use of this herb include gastrointestinal discomfort such as nausea, abdominal pain, or diarrhea. Some individuals may also experience allergic reactions which might manifest as rashes, itching, or swelling. These responses are typically related to pre-existing sensitivities to Echinacea or its related plant family, the Asteraceae.
Individuals with known allergies to plants within the Asteraceae family, such as ragweed, marigolds, or daisies, should exercise caution, as they may have heightened susceptibility to adverse reactions. Moreover, those suffering from autoimmune conditions like lupus, multiple sclerosis, or rheumatoid arthritis should avoid Echinacea due to its modulating effects on the immune system. In such cases, Echinacea might exacerbate symptoms or interact unfavorably with other treatments.
Pregnant and nursing women should consult with a healthcare provider before incorporating Echinacea into their regimen. Although there is limited research on its effects during pregnancy and lactation, it is advisable to err on the side of caution. Similarly, individuals currently taking prescription medications or managing chronic ailments must seek professional medical advice to preempt possible drug-herb interactions. This step ensures not only the safety but also the efficacy of their overall treatment plan.
As with any herbal supplement, the importance of professional guidance cannot be overstated. Consulting with a healthcare professional, such as a physician or a certified herbalist, offers valuable personalized insights. They can help determine whether Echinacea is appropriate and safe based on the individual’s health profile, ensuring a balanced and well-informed approach to wellness.
“`
Información adicional
| color | Black, Red |
|---|---|
| shoe-size | 7, 7.5, 8, 8.5, 9, 9.5 |












Valoraciones
No hay valoraciones aún.