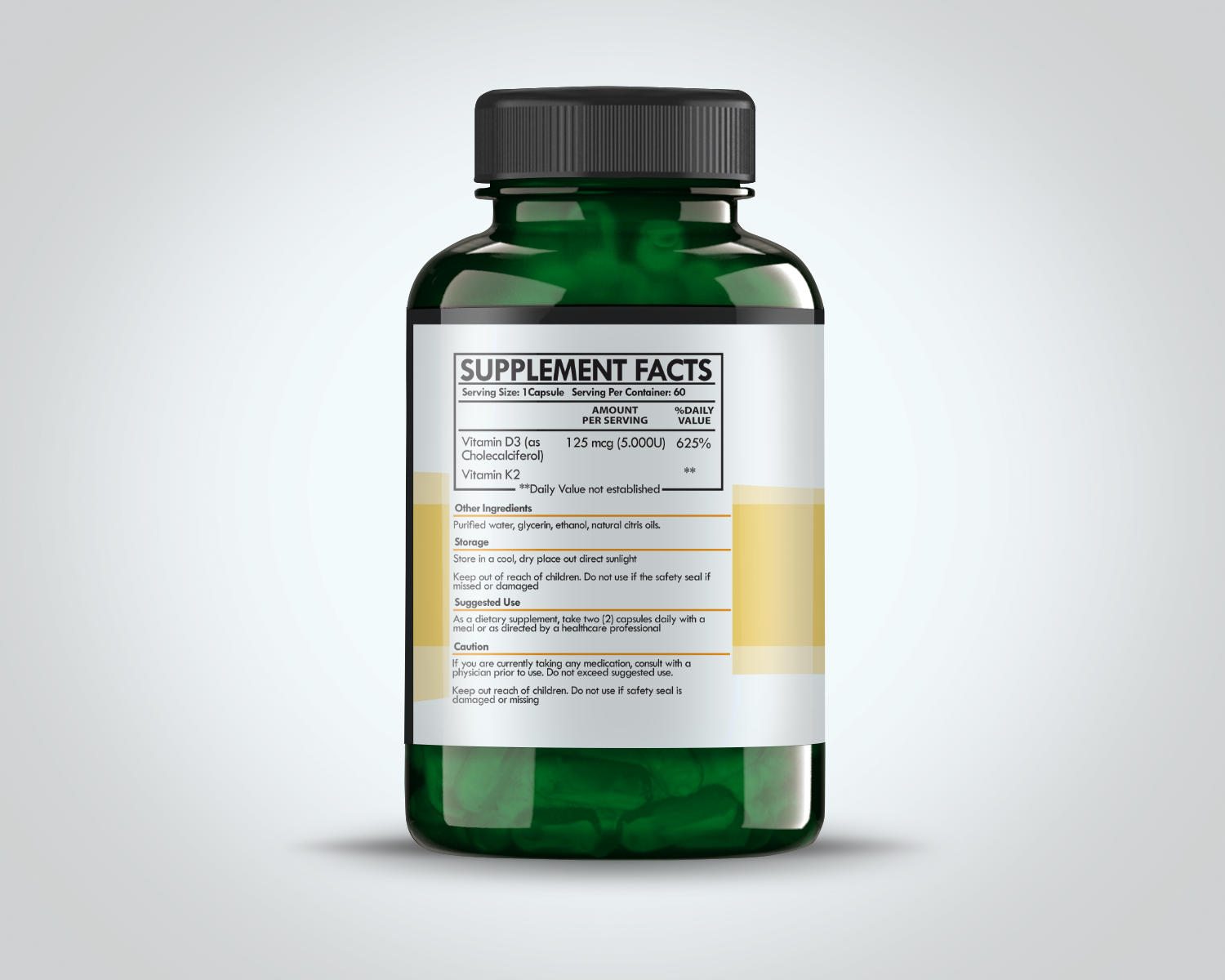
Vitamins K2 and D3 are crucial micronutrients that play significant roles in maintaining overall health. Vitamin K2, a subset of the vitamin K group, is structurally characterized by its various menaquinone forms, with MK-7 being the most studied. Vitamin D3, or cholecalciferol, belongs to the vitamin D family and is known for its synthesis in the skin upon exposure to sunlight.
Nutraplus Vitamin K2 + D3
$7.99
Descripción
Introduction to Vitamins K2 and D3
Vitamins K2 and D3 are crucial micronutrients that play significant roles in maintaining overall health. Vitamin K2, a subset of the vitamin K group, is structurally characterized by its various menaquinone forms, with MK-7 being the most studied. Vitamin D3, or cholecalciferol, belongs to the vitamin D family and is known for its synthesis in the skin upon exposure to sunlight.
The historical context of these vitamins spans several decades. Vitamin K2 was discovered in the 1930s by Henrik Dam when researching the causes of hemorrhage in chickens. Vitamin D3’s discovery predates this, traced back to the early 20th century during studies on rickets, leading to the understanding that sunlight exposure could remedy this condition.
The dietary sources of vitamins K2 and D3 are diverse. Vitamin K2 is predominantly found in animal-based foods such as cheese, egg yolks, and fermented products like natto. Vitamin D3, on the other hand, is primarily sourced from fatty fish, liver, and fortified foods. Both vitamins play pivotal roles in the body, but their mechanisms of action differ.
Vitamin K2 is essential for the activation of proteins responsible for blood clotting and calcium regulation. It ensures calcium is deposited in bones and teeth, helping to prevent arterial calcification. Vitamin D3 facilitates calcium absorption in the gut and maintains serum calcium and phosphate levels, which is vital for bone formation and remodeling. Both vitamins are inextricably linked to bone health, cardiovascular function, and beyond.
Understanding the distinct yet complementary roles of vitamin K2 and D3 sets the stage for a deeper exploration into their synergistic effects. This foundational knowledge allows for a comprehensive appreciation of their combined potential in promoting better health outcomes. As we delve into their specific benefits and interactions, the intricate dance between these two vitamins will become apparent, highlighting their indispensable contributions to human health.
The Health Benefits of Vitamin K2
Vitamin K2 plays a critical role in maintaining cardiovascular health, primarily by preventing arterial calcification. Research has shown that Vitamin K2 activates matrix Gla-protein (MGP), a potent inhibitor of arterial calcification. This mechanism is crucial in supporting heart function and reducing the risk of coronary artery disease. A longitudinal study published in the Journal of Nutrition demonstrated that higher dietary intake of Vitamin K2 was associated with a lower incidence of cardiovascular ailments.
Beyond its cardiovascular benefits, Vitamin K2 is indispensable for bone health. It assists in the regulation of calcium by activating osteocalcin, a protein essential for binding calcium to the bone matrix. This process not only promotes stronger bones but also prevents calcium from depositing in the arteries, a dual benefit for bone and heart health. Epidemiological studies have underscored that adequate Vitamin K2 intake can significantly reduce the risk of osteoporosis and fractures in aging populations.
Moreover, emerging evidence suggests that Vitamin K2 may have positive effects on dental health. It plays a role in the remineralization process of teeth, potentially reducing the incidence of cavities. Additionally, Vitamin K2 has been linked to cognitive function. A study published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease suggested that Vitamin K2 might contribute to improved brain health by preventing oxidative damage and supporting nerve cell function.
Lastly, Vitamin K2 is being investigated for its possible effects on cancer treatment. Preliminary research indicates that Vitamin K2 may induce apoptosis in cancer cells, thereby inhibiting their growth. While more extensive clinical trials are needed, these initial findings are promising and add to the growing list of health benefits associated with this vital nutrient.
In conclusion, the importance of adequate Vitamin K2 intake cannot be overstated. Its multifaceted benefits, from heart and bone health to potential roles in dental health, cognitive function, and cancer treatment, underscore its essential place in our diet for overall well-being.
The Health Benefits of Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3, also known as cholecalciferol, is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a pivotal role in numerous physiological processes. One of its most well-known functions is in aiding calcium absorption, which is essential for maintaining strong bones and teeth. By promoting calcium uptake in the intestines, Vitamin D3 helps prevent conditions such as rickets in children, characterized by soft and weak bones, and osteoporosis in adults, where bones become brittle and susceptible to fractures.
Research has highlighted the significance of Vitamin D3 in immune system support. Adequate levels of this vitamin are crucial for the activation of T cells, which are essential for the adaptive immune response. By strengthening immune defenses, Vitamin D3 not only aids in the prevention of common infections, such as colds and the flu, but also contributes to the management of autoimmune diseases, including multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis. A study in the “British Journal of Nutrition” found that individuals with adequate Vitamin D3 levels had a 50% higher chance of recovering from upper respiratory infections compared to those with deficiencies.
Moreover, emerging research underscores Vitamin D3’s influence on mood regulation and mental health. There is growing evidence linking this vitamin to a reduced risk of depression and improved emotional well-being. An article in the “Journal of Affective Disorders” revealed that individuals with higher levels of Vitamin D3 were 30% less likely to experience depressive symptoms. This correlation is thought to be due to Vitamin D3’s role in the synthesis of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that affects mood stability.
In summary, Vitamin D3 is indispensable for maintaining bone health, bolstering the immune system, and enhancing mental well-being. The integration of this essential nutrient into one’s daily regimen, either through sunlight exposure, diet, or supplementation, can markedly improve overall health and quality of life.
Synergy Between Vitamin K2 and D3
The interplay between Vitamin K2 and Vitamin D3 exemplifies a compelling synergy in the realm of nutritional science, particularly regarding the optimization of calcium metabolism. Both vitamins are indispensable in their own right, but when working in concert, they exhibit augmented benefits that surpass their individual roles, ensuring calcium is effectively utilized and deposited where it is most beneficial – in bones and teeth – while preventing its harmful accumulation in arteries and other soft tissues.
Vitamin D3 is renowned for its ability to enhance calcium absorption in the gut, significantly aiding in the elevation of circulating calcium levels in the bloodstream. However, the efficient utilization of this absorbed calcium mandates the presence of Vitamin K2. Vitamin K2 activates key proteins such as osteocalcin and matrix Gla-protein (MGP), which facilitate the deposition of calcium into the bone matrix and inhibit its deposition in arterial walls and other soft tissues, respectively.
The symbiotic relationship between these vitamins is well-documented in various clinical studies. Research indicates that supplementation with both Vitamin K2 and D3 leads to improved bone mineral density and cardiovascular health compared to supplementation with either vitamin alone. For instance, a study published in “Osteoporosis International” highlighted that postmenopausal women taking combined Vitamin K2 and D3 supplements exhibited significantly lower risks of fractures and arterial stiffness than those taking placebos or individual vitamins.
Optimal dosage and dietary sources are crucial to harnessing the synergistic effects of these vitamins. For adults, a common recommendation for Vitamin D3 is 1,000 IU to 4,000 IU per day, depending on individual needs and health status. Vitamin K2, particularly in the form of MK-7, is often recommended at 100 to 200 mcg per day. Dietary sources such as fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and fermented foods like natto and certain cheeses are excellent options for these vitamins.
When considering supplementation, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to determine personalized needs based on diet, lifestyle, and medical history. This ensures that combined Vitamin K2 and D3 supplementation can be effectively optimized for bone health and cardiovascular protection, enhancing overall well-being.










Valoraciones
No hay valoraciones aún.